Mike G, DeSmogBlog, Waking Times
When NASA researchers first saw data indicating a massive cloud of methane floating over the American Southwest, they found it so incredible that they dismissed it as an instrument error.
But as they continued analyzing data from the European Space Agency’s Scanning Imaging Absorption Spectrometer for Atmospheric Chartography instrument from 2002 to 2012, the “atmospheric hot spot” kept appearing.
The team at NASA was finally able to take a closer look, and have now concluded that there is in fact a 2,500-square-mile (6,500 square kilometers) cloud of methane—roughly the size of Delaware—floating over the Four Corners region, where the borders of Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah all intersect.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Michigan
A report published by the NASA researchers in the journal Geophysical Research Letters concludes that “the source is likely from established gas, coal, and coalbed methane mining and processing.” Indeed, the hot spot happens to be above New Mexico’s San Juan Basin, the most productive coalbed methane basin in North America.
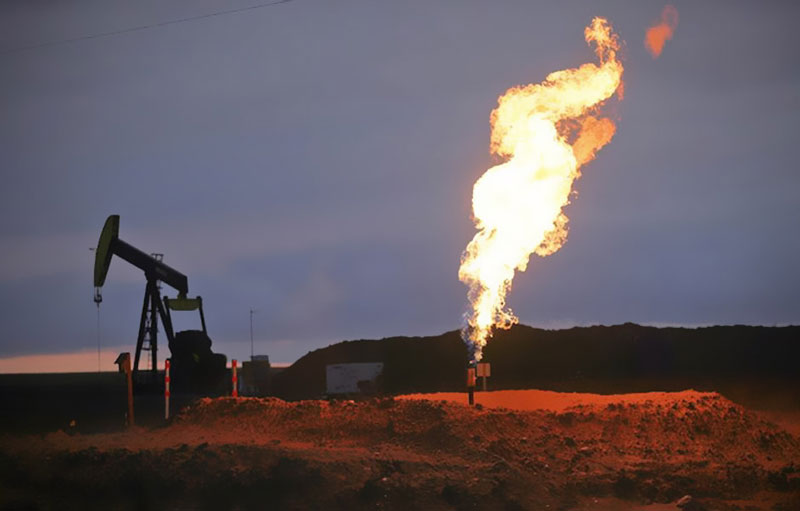
Methane is 20-times more potent as a greenhouse gas than CO2, and has been the focus of an increasing amount of attention, especially in regards to methane leaks from fracking for oil and natural gas. Pockets of natural gas, which is 95-98% methane, are often found along with oil and simply burned off in a very visible process called “flaring.” But scientists are starting to realize that far more methane is being released by the fracking boom than previously thought.
Earlier this year, Cornell environmental engineering professor Anthony Ingraffea released the results of a study of 41,000 oil and gas wells that were drilled in Pennsylvania between 2000 and 2012, and found newer wells using fracking and horizontal drilling methods were far more likely to be responsible for fugitive emissions of methane.
According to the NASA researchers, the region of the American Southwest over which the 2,500-square-mile methane cloud is floating emitted 590,000 metric tons of methane every year between 2002 and 2012—almost 3.5 times the widely used estimates in the European Union’s Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research—and none of it was from fracking.
That should prompt a hard look at the entire fossil fuel sector, not just fracking, according to University of Michigan Professor Eric Kort, the lead researcher on the study:
“While fracking has become a focal point in conversations about methane emissions, it certainly appears from this and other studies that in the US, fossil fuel extraction activities across the board likely emit higher than inventory estimates.”
~~ Help Waking Times to raise the vibration by sharing this article with friends and family…
Be sure to check out our article: